4.7.1 Background
Existing Fuji machines support both backlight and frontlight systems, however, the newly developed NXT machines support frontlight only.
As a result, it is necessary to convert existing part data created for used with a backlight system to enable the part to be processed using a frontlight system.
The NXT machines are equipped with a feature that enables automatic conversion of part data created for backlight systems, however, there are cases whereby it is necessary to make a setting at the “Override” field in Fuji Flexa for the part data of certain parts. This section provides a compatibility table for the part data of existing machines and the NXT machines, as well as details of limitations relating to the part data conversion process.
It is important to point out that when making new part data, use the old vision type and p patterns if the data is to be used on other Fuji machines. If the data is never to be used on older Fuji machines (only NXTs are present), then use the NXT vision types and the frontlight p_patterns.
4.7.2 Vision type compatibility table for the NXT
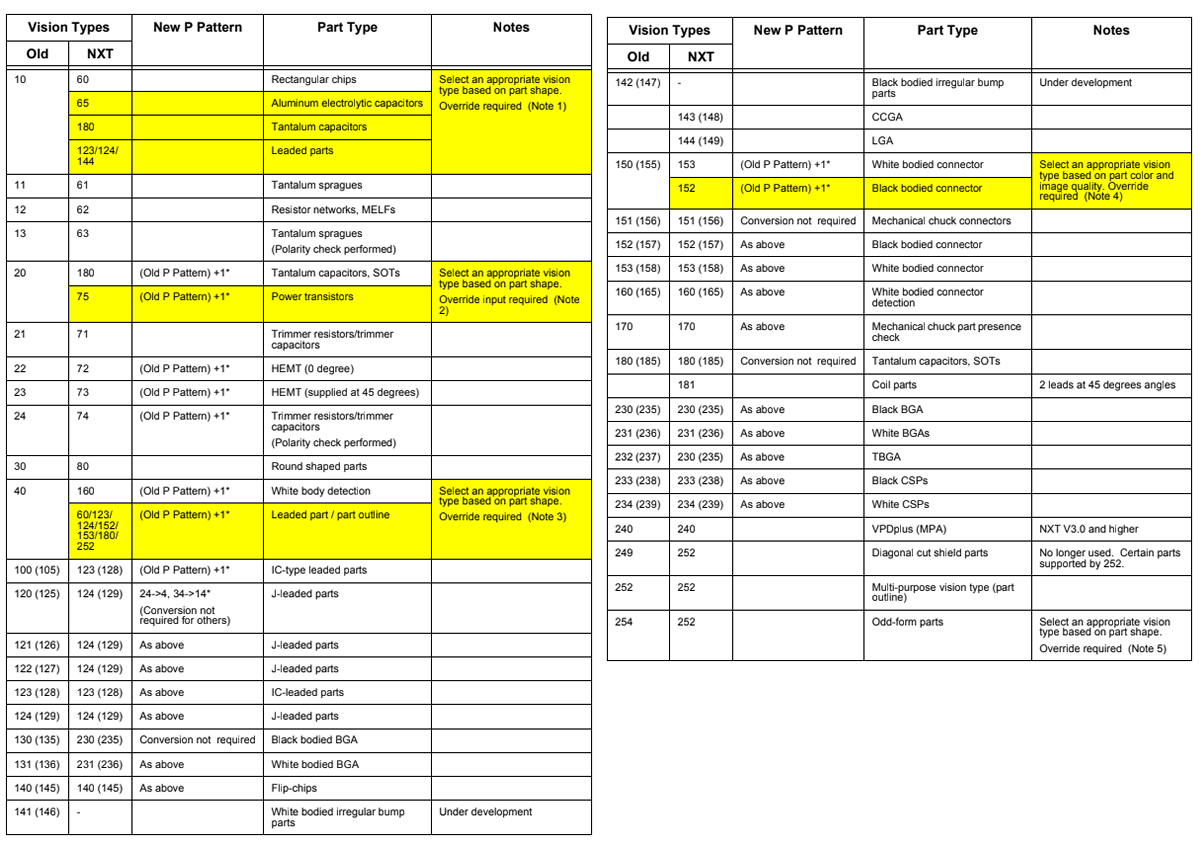
Note: The p pattern is automatically converted if the old vision type is in the “generic” section.
Note: The shaded areas represent the vision types for which automatic conversion is not supported by the NXT machines. All other vision types are supported and therefore require no additional data entry.
Note 1
Previously, it was possible to perform vision processing for all rectangular chips using vision type 10, however, when using frontlighting, due to the influence of leads and so forth on the body of the part, it is necessary to separate those parts previously supported by vision type 10 into four types as detailed in the table below.
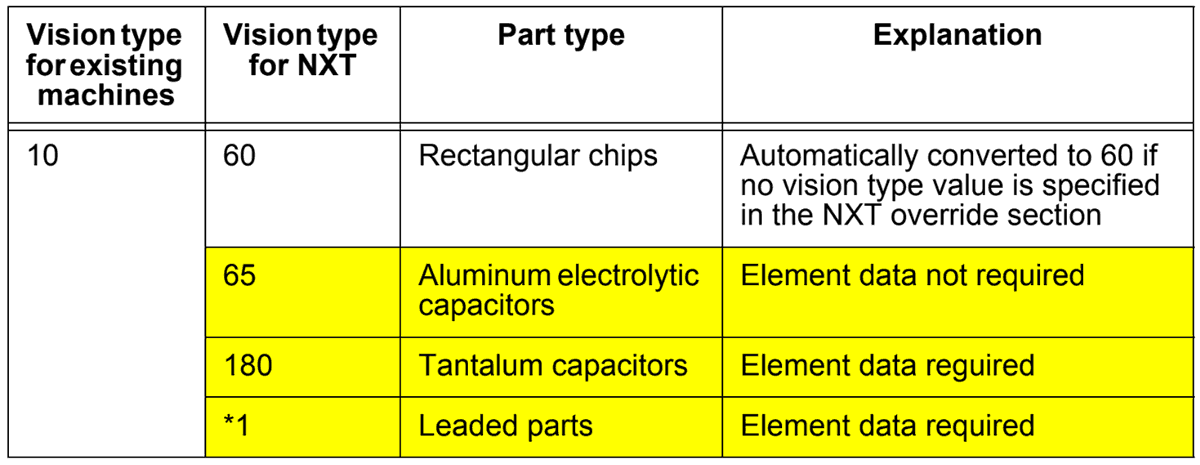
*1: There are cases where none of the vision types in the above table are applicable. Some examples of such parts are rectangular parts other than rectangular chips, tantalum capacitors, or aluminum electrolytic capacitors with multiple leads inside the edge of the part body. In this case, select an appropriate vision type from 123, 124, 144, or 180 and enter element information for the leads based on the shape of the part.
Note: Vision type 10 is automatically converted to 60, however, if another value has been specified in the override vision type value for the NXT, this value will be used.
Note: Refer to 4.6.2 “NXT vision types” for details on how to create lead data.
Note 2
Vision type 20 is used on existing machines to process SOT-type parts with few leads, however, on the NXT machines, vision type 180 is used. A custom vision type is used for power transistors.
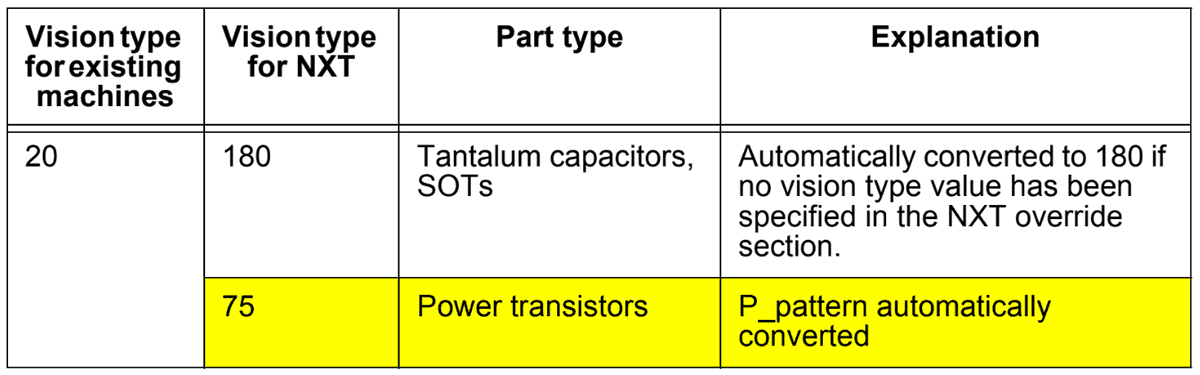
Note: Vision type 20 is automatically converted to 180, however, if another value has been specified in the override vision type value for the NXT, this value will be used.
Note 3
Vision type 40 is used on existing machines to process parts with backlighting, using the calculated body position as the placing reference point. The NXT machine, however, can use either the body center or part center for the leaded (bumped) type parts. As a result, there is no need to select a custom vision type. Select the appropriate vision type from the following table based on the part type.
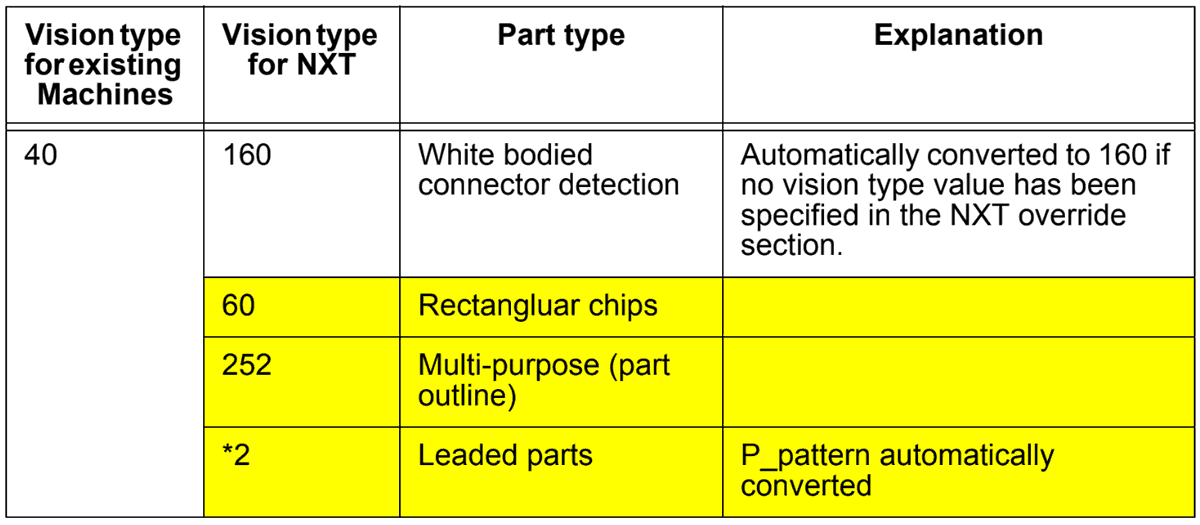
*2: Use the appropriate vision type (123, 124, 152, 153, or 180) depending on the leads and the lead quantity.
Note: Vision type 40 is automatically converted to 160, however, if another value has been specified in the override vision type value for the NXT, this value will be used.
Note 4
Vision type 150 is used on existing machines to process connectors with backlighting, however, this vision type has now been separated as shown in the table below based on body color.
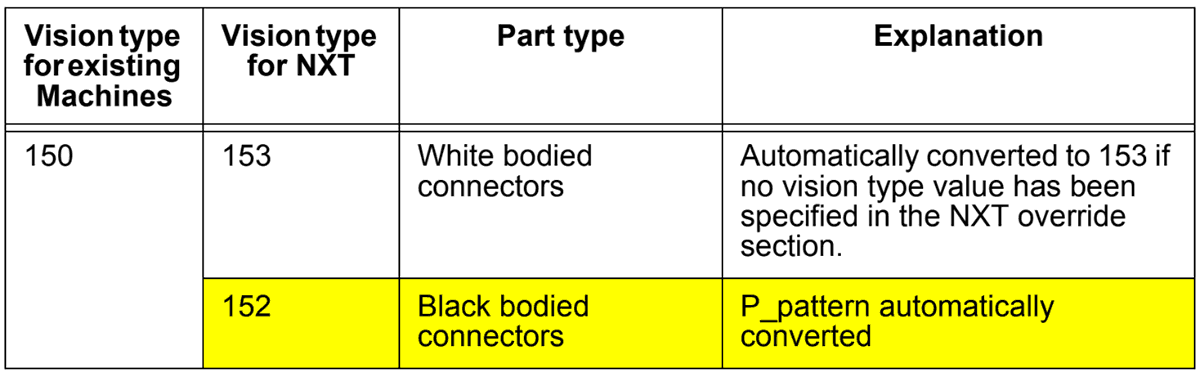
Note: Vision type 150 is automatically converted to 153, however, if another value has been specified in the override vision type value for the NXT, this value will be used.
Note 5
Vision type 254 is used on existing machines to place odd-form parts using backlight. On NXT machines, this vision type has been changed as shown in the table below.
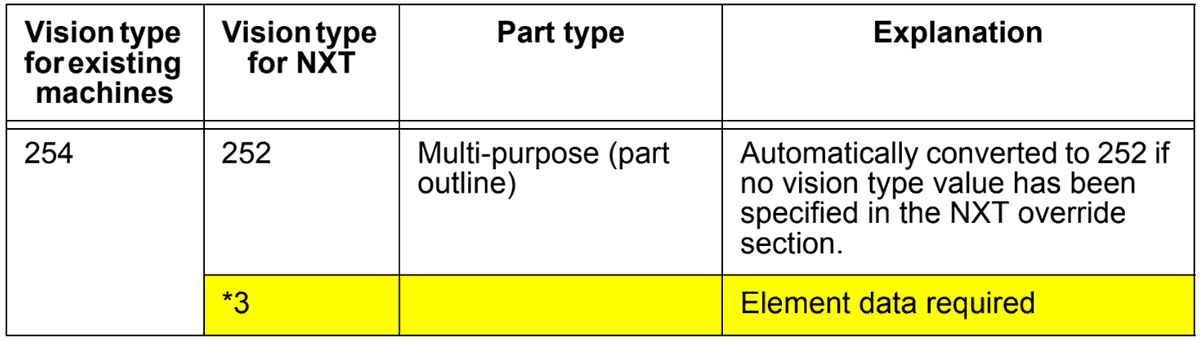
*3: On existing machines, vision type 254 uses backlighting to place parts that cannot be placed using other vision types, however, as NXT machines use only frontlighting, it is necessary to choose the most appropriate vision type available. Select vision type 252 when placing white bodied parts with no leads. Vision type 252 can also be used for white bodies parts with leads that are part of the body. If using a different vision type, element data will be required depending on the selected vision type.
Note: Vision type 254 is automatically converted to 252, however, if another value has been specified in the override vision type value for the NXT, this value will be used.